π-Conjugated Carbon-Based Materials for Infra-Red Thermal Imaging
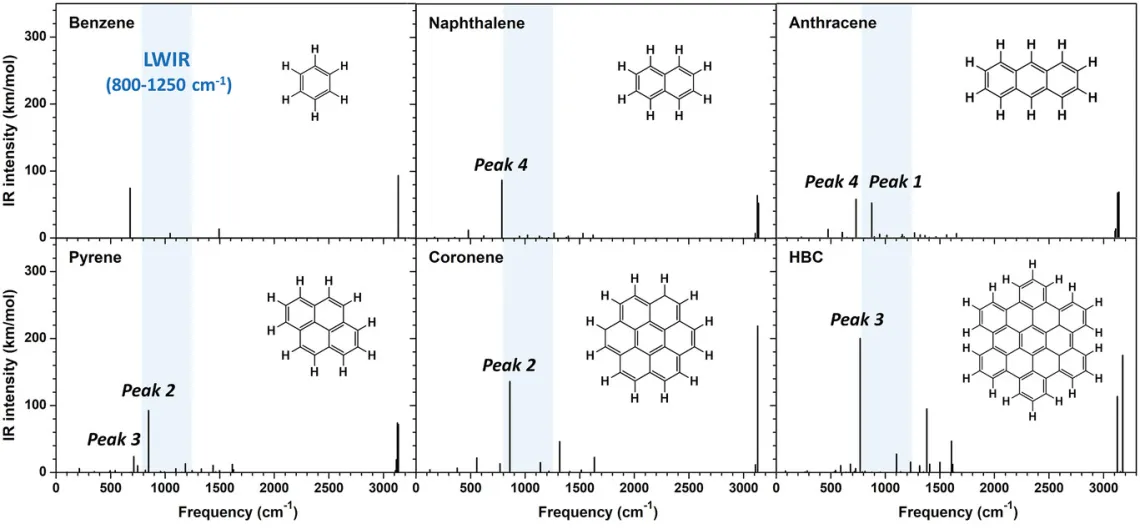
Infrared (IR) thermal imaging is receiving a great deal of attention due to its wide range of applications. Given multiple issues (like cost and availability) with the inorganic materials currently exploited for IR imaging, there is nowadays a great push of developing organic imaging materials. Carbon-based materials are known to have significant transparency in the visible and IR regions and some are used as transparent conductors. Here, whether π-conjugated carbon-based materials are suitable for long-wave (LW) and mid-wave (MW) IR imaging applications is computationally assessed. Using density functional theory calculations, the IR-vibrational properties of molecules from acenes to coronenes and fullerenes, and of periodic systems like graphene and carbon nanotubes are characterized. Fullerenes, graphenes, and double-walled carbon nanotubes are found to be very attractive as they are transparent in both the LWIR and MWIR regions, a feature resulting from the absence of hydrogen atoms. Also, it is found that replacing hydrogen atoms in a molecule with deuterium or sulfur atoms can be an efficient way to improve their LWIR or MWIR transparency, respectively. For fused-ring systems having hydrogen atoms on the periphery, designing molecules with trio CH-units is another way to enhance the transparency in the LWIR region.
